Daijiworld Media Network – New Delhi
New Delhi, Aug 23: Mosquitoes may be small, but the diseases they spread pose some of the gravest threats to human health. Known as the deadliest animals on Earth, they transmit several illnesses—many of which have no cure. Here’s a look at mosquito-borne diseases with no specific treatment:
Japanese Encephalitis
Caused by a flavivirus and transmitted by Culex mosquitoes in parts of Asia and the Western Pacific, Japanese encephalitis is often mild or asymptomatic. Severe cases, however, can lead to high fever, seizures, brain inflammation, and permanent neurological damage. There is no treatment for the virus; only symptoms can be managed.
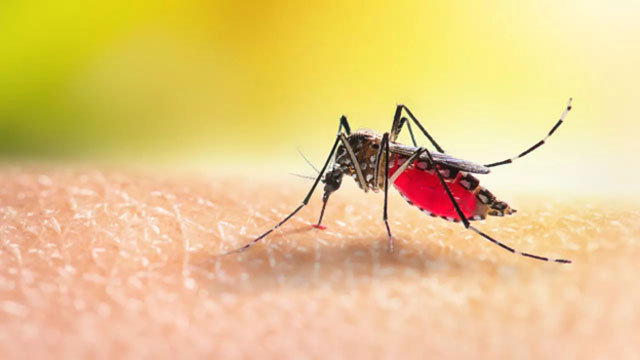
Dengue Fever
Dengue virus (DENV) spreads through infected mosquitoes and affects 100–400 million people annually, according to WHO. Symptoms include high fever, severe headaches, joint pain, and in severe cases, hemorrhagic fever which can be fatal. No specific treatment exists; care focuses on symptom management.
Zika Virus
Transmitted by Aedes mosquitoes, Zika virus infection is often asymptomatic but can cause serious complications for pregnant women, including severe birth defects like microcephaly. There is no antiviral treatment; management is limited to rest, fluids, and medication for symptoms.
Chikungunya
Spread by Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus mosquitoes, chikungunya causes fever and severe joint pain that may last weeks or months. While death is rare, prolonged arthritis-like symptoms can affect quality of life. There is no specific medicine; only symptom relief is possible.
West Nile Virus
West Nile virus can cause fatal neurological disease. Though 80% of infections are asymptomatic, severe cases may include headache, high fever, neck stiffness, disorientation, paralysis, and coma. No medicine or vaccine is currently available, and antibiotics are ineffective.
Yellow Fever
Found in Africa and South America, yellow fever is transmitted by Aedes aegypti mosquitoes. Symptoms range from fever, chills, muscle pain, and nausea to severe jaundice and bleeding. There is no cure, though vaccination is available for prevention.